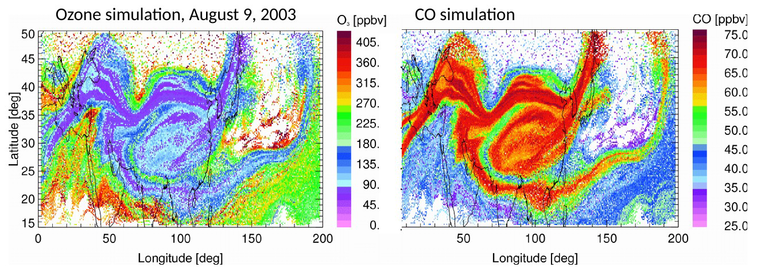
Transport and mixing in the Asian summer monsoon at 18km altitude. AtmoSat will be unprecedented to resolve the fine filaments facilitating tracer transport and mixing.
The stratospheric Brewer-Dobson circulation and stratosphere-troposphere exchange have a strong impact on the on the variability of water vapour, ozone ans sulfate aerosols in the upper troposphere and stratosphere. By providing unique measurements of transport tracers such as sulfur hexafluoride, methane, nitrous oxides, methane and fluorocarbons, AtmoSat contributes to a significantly improved understanding of these processes, their spatial and temporal variability, and their impact on global and regional climate.
Major scientific messages in the literature:
- The intensity of Brewer-Dobson circulation can be diagnosed by the age of stratospheric air:
Stiller et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2012
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/12/3311/2012/
Haenel et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2015
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/15/13161/2015/acp-15-13161-2015.html
- Changes in air age suggest a change in stratospheric circulation patterns:
Stiller et al., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2017
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/17/11177/2017/
- While climate models predict a generally accelerated residual circulation, the observations do not indicate a clear trend over the last decades:
Engel et al., Nature Geoscience, 2009
https://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo388
Waugh, Nature Geoscience, 2009
https://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo397
- AtmoSat will be the only dataset that will reliably predict these changes in the future:
von Clarmann and Grabowski, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2016
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/16/14563/2016/